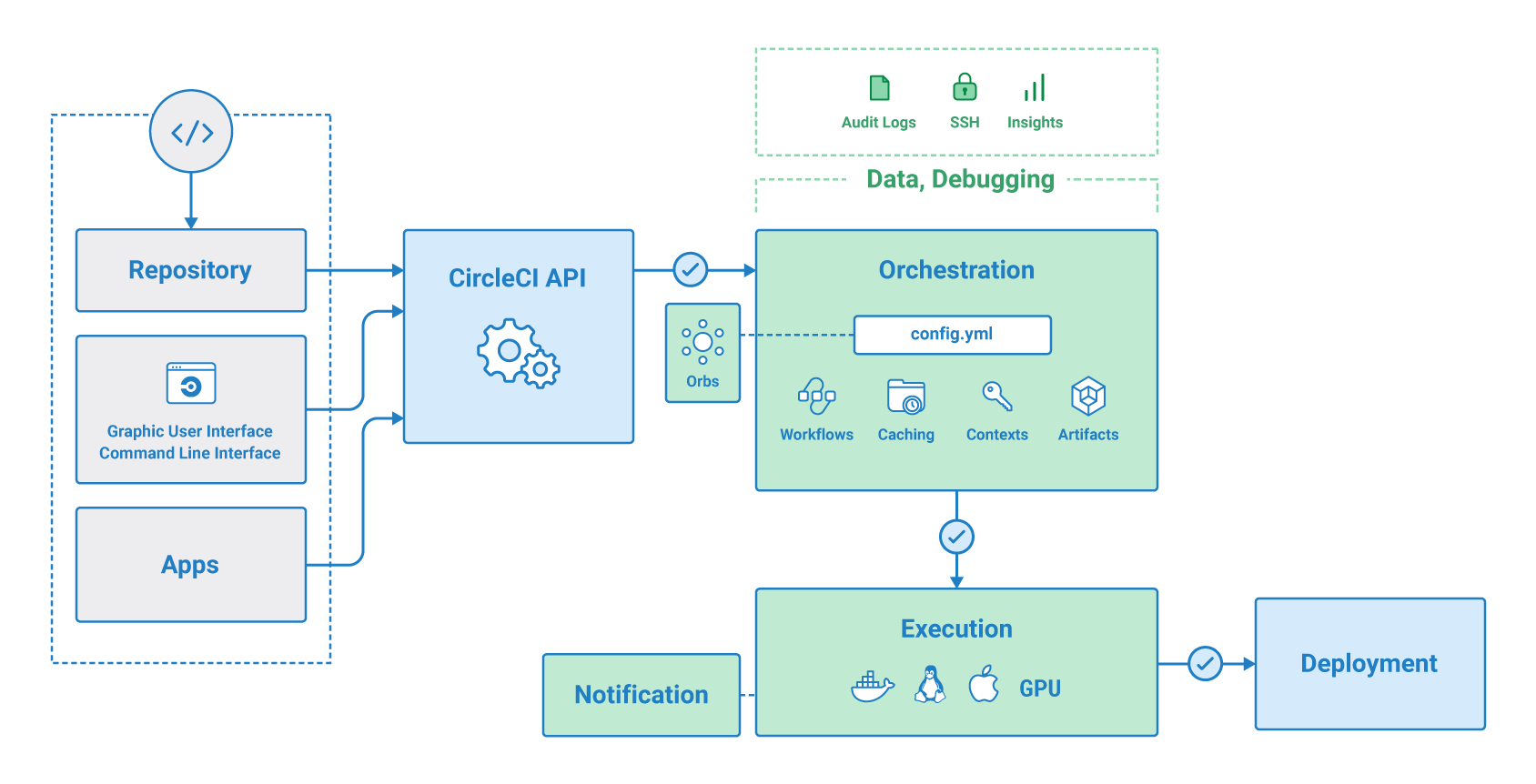
# CircleCI
CircleCI 可以绑定 GitHub/Bitbucket,只要你的代码有变更,就会自动抓取,根据你的配置,提供运行环境,执行测试、构建和部署。
所以,通过 CircleCI 我可以快速方便的实现持续集成和持续部署。
# 基础配置
版本:指定使用的 CircleCI 版本。
# 指定要使用的 CircleCI 版本
version: 2
工作流:工作流定义了一系列的任务和他们的运行顺序。它可以使任务并行,穿行和按计划或者手动控制运行。
workflows:
version: 2
one_and_two: # this is the name of our workflow
jobs:
- one
- two:
requires:
- one # wait for one job to complete successfully before starting
在上面的 one_and_two 工作流中我们包含了 one、two 两个任务,任务是步骤的集合:
jobs:
one: # this is the name of our first job.
docker: # it uses the docker executor
- image: circleci/ruby:2.4.1 # specifically, a docker image with ruby 2.4.1
# Steps are a list of commands to run inside the docker container above.
steps:
- checkout # this pulls code down from GitHub
- run: echo "A first hello" # This prints "A first hello" to stdout.
- run: sleep 25 # a command telling the job to "sleep" for 25 seconds.
two:
docker:
- image: circleci/ruby:2.4.1
steps:
- checkout
- run: echo "A more familiar hi"
- run: sleep 15
如上可见,步骤一般是可执行的命令组成的。
# Workspaces
每个工作流都有一个关联的工作空间,可用于在工作流进行时将文件传输到下游作业,此时我们需要使用 persist_to_workspace 键。
文件和目录中的带有 paths 的属性使用 persist_to_workspace 会被上传到工作区中的临时目录中,相对于 root 键定义的目录。文件和目录在这时上传之后,就可以在相应的子任务中使用。
配置任务接收存储的数据时,需要用到 attach_workspace 键。
version: 2
jobs:
one:
docker:
- image: circleci/ruby:2.4.1
steps:
- checkout
- run: echo "A first hello"
- run: mkdir -p my_workspace
- run: echo "Trying out workspaces" > my_workspace/echo-output
- persist_to_workspace:
# Must be an absolute path, or relative path from working_directory
root: my_workspace
# Must be relative path from root
paths:
- echo-output
two:
docker:
- image: circleci/ruby:2.4.1
steps:
- checkout
- run: echo "A more familiar hi"
- attach_workspace:
# Must be absolute path or relative path from working_directory
at: my_workspace
- run: |
if [[ $(cat my_workspace/echo-output) == "Trying out workspaces" ]]; then
echo "It worked!";
else
echo "Nope!"; exit 1
fi
workflows:
version: 2
one_and_two:
jobs:
- one
- two:
requires:
- one
在这里 (opens new window)阅读有关工作区的更多信息。
# SSH into Your Build
当出现问题时,我们可能需要对问题进行调试,这时后我们可以通过 SSH 直接在 CircleCI jobs 中执行操作。
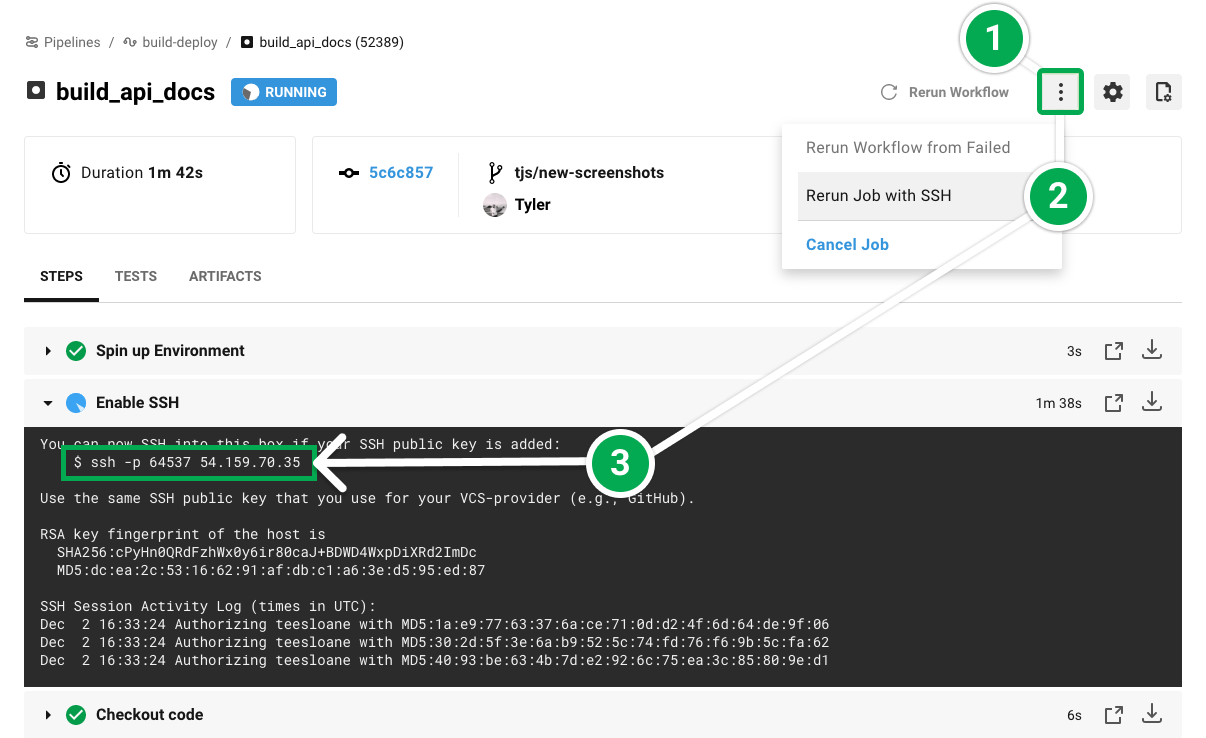
使用以下命令,查看是否可以找到并查看使用工作空间创建的文件的内容:
pwd # print what directory, find out where you are in the file system
ls -al # list what files and directories are in the current directory
cd <directory_name> # change directory to the <directory_name> directory
cat <file_name> # show me the contents of the file <file_name>
# 减少重复的指令
通过 YAML 语法的特性,你可以将重复的指令统一放到一个地方来进行引用。
defaults: &defaults
adapter: postgres
host: localhost
development:
database: myapp_development
<<: *defaults
test:
database: myapp_test
<<: *defaults
相当于:
defaults:
adapter: postgres
host: localhost
development:
database: myapp_development
adapter: postgres
host: localhost
test:
database: myapp_test
adapter: postgres
host: localhost
其中 & 用来建立锚点(defaults),<< 表示合并到当前数据,* 用来引用锚点。
